Why Use HC-SR04 and ESP32?
If you’ve ever wanted your projects to “see” how far away something is, the HC-SR04 ultrasonic sensor is a beginner-friendly and budget-friendly option. When paired with the ESP32, you not only get accurate distance measurements but also open the door to Wi-Fi- or Bluetooth-enabled applications, from smart parking assistants to IoT-based distance monitoring dashboards.
The ESP32’s extra processing power and built-in connectivity make it ideal for projects that go beyond simple distance sensing. Imagine checking the distance to your water tank level from your phone, or logging obstacle data to a cloud service in real-time. All possible with this combo.
What is the Ultrasonic Sensor HC-SR04?
The Ultrasonic Sensor HC-SR04 is a popular, low-cost, and easy-to-use sensor that measures the distance to objects using ultrasonic sound waves. It’s widely used in robotics, automation, and object detection systems.
The sensor works by sending out ultrasonic waves through a transmitter and measuring the time it takes for the echo to return to the receiver. The time taken is then converted into distance.

Key Specs You Should Know
- Operating Voltage: 5V
- Measuring Range: 2 cm – 400 cm
- Accuracy: ±3 mm
- Operating Frequency: 40 kHz
💡 ESP32 voltage tip: While the sensor runs on 5V, the ESP32’s GPIO pins are 3.3V tolerant. That means the ECHO pin needs a voltage divider or level shifter to avoid damaging your board.
How the HC-SR04 Works (In Simple Terms)
Think of the HC-SR04 like a bat:
- It sends out an ultrasonic “click” using its transmitter.
- That sound wave bounces off the nearest object and comes back.
- The sensor’s receiver picks it up and measures how long the journey took.
- Using the speed of sound, we can figure out the distance.
![]()
We divide by 2 because the sound travels to the object and back.
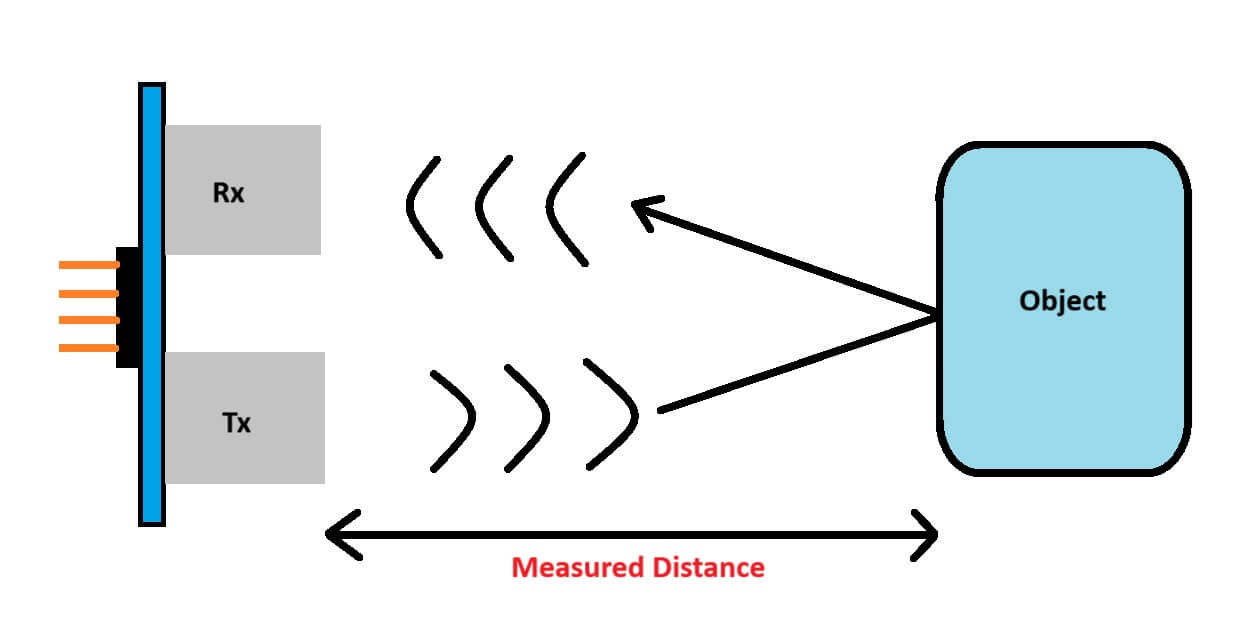
Read more about the working of Ultrasonic Sensors here.
Connecting HC-SR04 and ESP32
Components Required:
- 1x HC-SR04 Ultrasonic Sensor
- 1x ESP32 Board
- Jumper Wires
- Breadboard
Here’s a safe wiring setup:
| HC-SR04 Pin | ESP32 Connection |
|---|---|
| VCC | 5V pin |
| GND | GND |
| TRIG | GPIO 5 |
| ECHO | GPIO 18 (via voltage divider) |
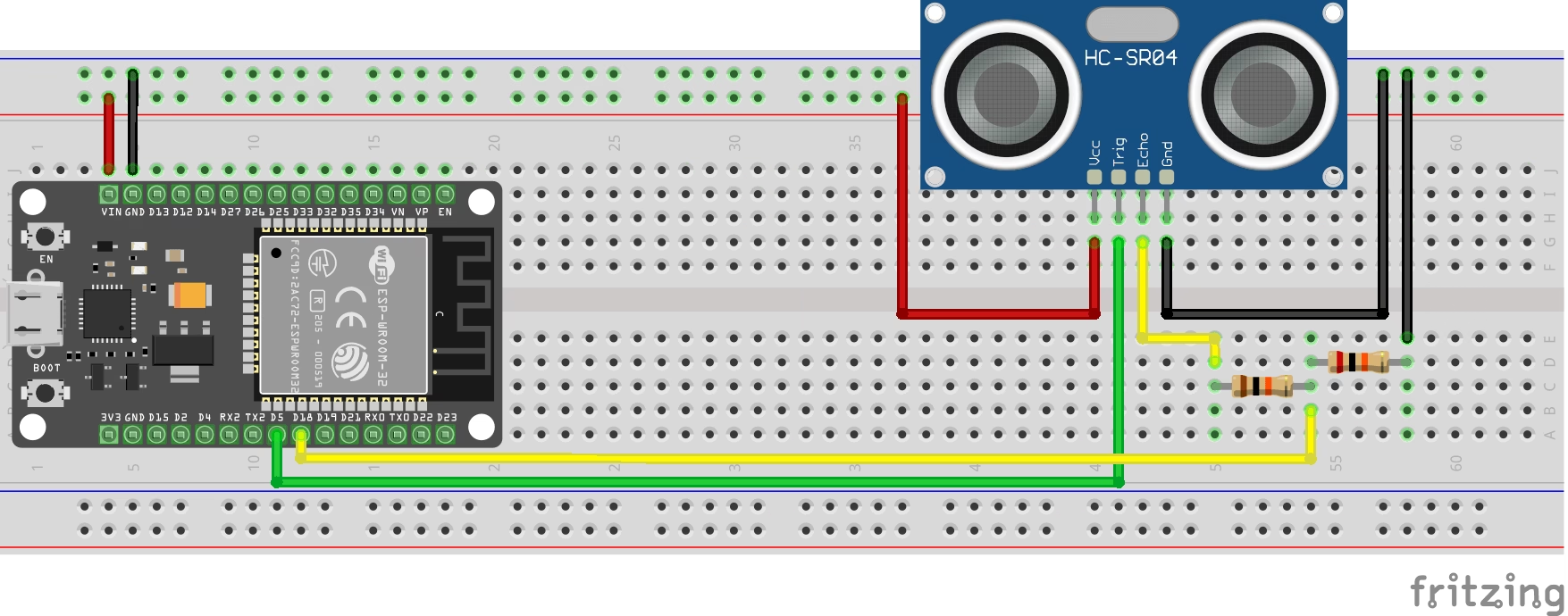
Voltage divider example:
Use two resistors (e.g., 10kΩ + 20kΩ) between the ECHO pin and ESP32 to drop the voltage from 5V to around 3.3V.
Example Code for ESP32
Here’s a simple test program to print distance values to the Serial Monitor.
// HC-SR04 and ESP32 Example
const int trigPin = 5; // TRIG connected to GPIO 5
const int echoPin = 18; // ECHO connected to GPIO 18 (via voltage divider)
long duration;
float distance;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200); // Faster baud rate for ESP32
pinMode(trigPin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(echoPin, INPUT);
}
void loop() {
// Send trigger pulse
digitalWrite(trigPin, LOW);
delayMicroseconds(2);
digitalWrite(trigPin, HIGH);
delayMicroseconds(10);
digitalWrite(trigPin, LOW);
// Read echo time
duration = pulseIn(echoPin, HIGH);
// Calculate distance (cm)
distance = duration * 0.0343 / 2;
Serial.print("Distance: ");
Serial.print(distance, 2); // Two decimal places
Serial.println(" cm");
delay(500);
}
Testing Your Setup
- Connect your ESP32 to the PC and upload the code using the Arduino IDE.
- Open the Serial Monitor at 115200 baud.
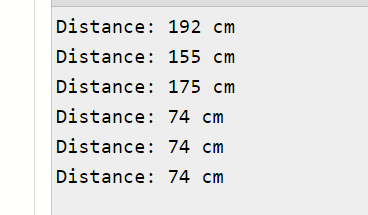
- Place objects at different distances and watch the readings update in real time.
If the readings look unstable, check your wiring, resistor values for the voltage divider, and ensure no reflective surfaces are causing false echoes.
Example Readings:
Ideas for ESP32 + HC-SR04 Projects
- IoT Water Tank Monitor – send level readings to a web dashboard.
- Smart Parking Assistant – LED or buzzer feedback when you’re too close.
- Automatic Door Opener – trigger a servo when someone approaches.
- Security Alarm – detect unexpected movement within a set range.
Common Troubleshooting Tips
- No readings? Check your wiring and make sure the ECHO pin isn’t directly connected to 5V logic.
- Inconsistent results? Avoid placing the sensor near fans, moving air, or angled surfaces.
- Weird high values? Ensure your
pulseIn()timeout is not too short, especially for long distances.
Final Thoughts
Using the HC-SR04 with ESP32 gives you reliable distance measurement while unlocking IoT capabilities the Arduino alone can’t offer. With just a few lines of code, you can start collecting and transmitting data for practical real-world applications.
Once you get the basics working, try integrating Wi-Fi or Bluetooth features; such as sending distance data to your phone or controlling devices automatically based on measured distance. The ESP32 makes it not only possible but surprisingly easy.
Explore More ESP32 Projects and Tutorials
If you enjoyed working with the HC-SR04 and ESP32, you might like these other guides on our website:
- How to Use DHT11 Temperature and Humidity Sensor with ESP32 – Learn to monitor environmental conditions in real-time.
- ESP32 with OLED Display – Show Sensor Readings – Perfect for visualizing distance or other sensor data on a compact screen.
- Building an IoT Water Level Monitor with ESP8266 – Take distance sensing to the next level with remote monitoring.
- Getting Started with ESP32 GPIO – Digital Input and Output – Master the basics before adding more sensors to your projects.
💡 These projects build on the skills you’ve learned here, so you can gradually create more advanced and connected systems.
