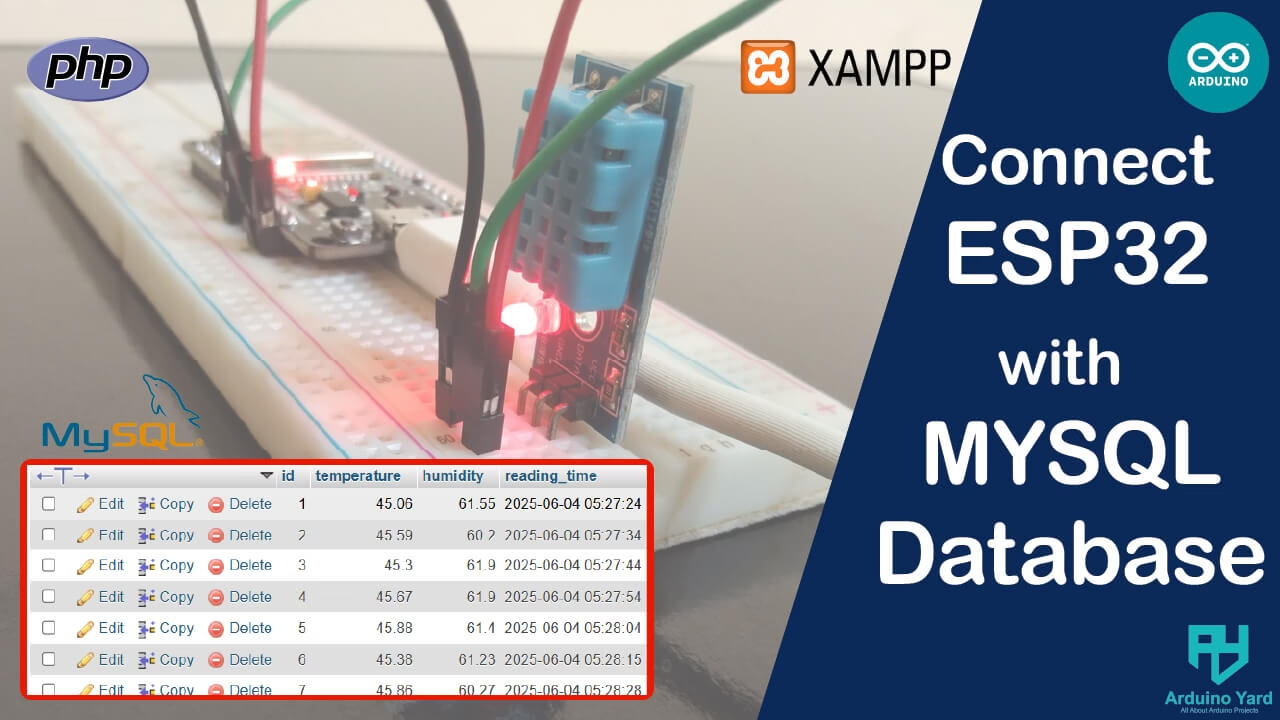
In this blog, we’ll walk you through a complete setup to send ESP32 data in MySQL database using XAMPP on a Windows PC.
In the world of IoT, collecting and storing sensor data is just as important as sending it. One of the most practical use cases is storing ESP32 data in MySQL using a local server like XAMPP. This allows you to create real-time dashboards, log data for analysis, or even trigger automated events based on sensor values.
Why Store ESP32 Data in MySQL?
The ESP32 is a powerful microcontroller with built-in Wi-Fi and Bluetooth capabilities, making it ideal for sending data from sensors. When you store ESP32 data in MySQL, you benefit from:
- Structured storage of time-series data
- Easy access via web interfaces (PHP, dashboards, etc.)
- Powerful querying for analytics
- Compatibility with BI tools, mobile apps, and cloud migration
By combining the ESP32 with XAMPP (which includes Apache, MySQL, and PHP), you can build a full-stack IoT application without any external services.
What You Need
Before we start, make sure you have the following:
- ESP32 board
- DHT11
- Arduino IDE (with ESP32 board package installed)
- XAMPP installed and running on Windows
- Basic knowledge of PHP and MySQL
- Local Wi-Fi connection
Step 1: Set Up XAMPP and MySQL Database
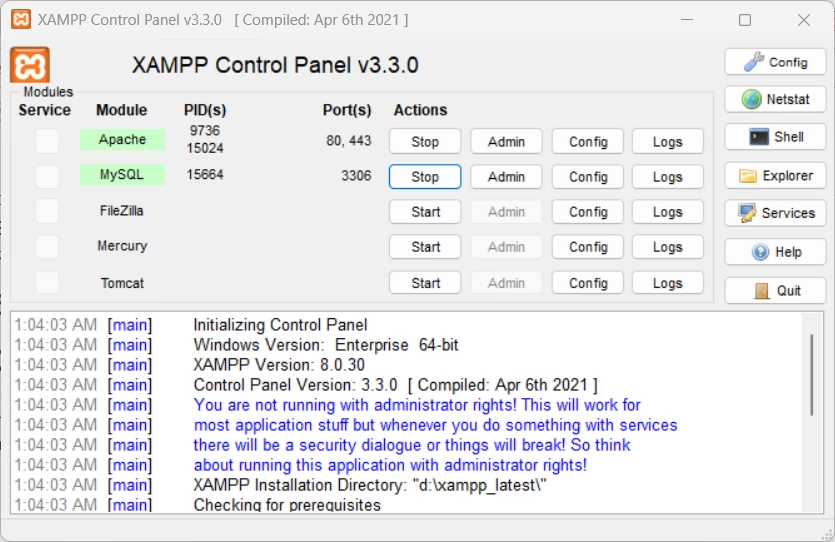
1. Start XAMPP
- Launch the XAMPP Control Panel
- Start Apache and MySQL
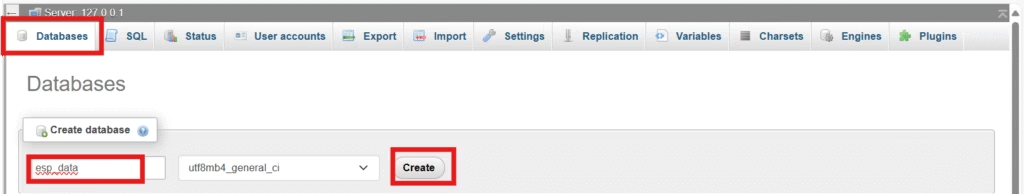
2. Create MySQL Database and Table
- Open your browser and go to
http://localhost/phpmyadmin - Click on Databases, create a new one named
esp_data - Click on the new database, then SQL.
Then click on SQL, and run this SQL command:
CREATE TABLE sensor_data (
id INT AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY,
temperature FLOAT,
humidity FLOAT,
reading_time TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP
);
As shown:
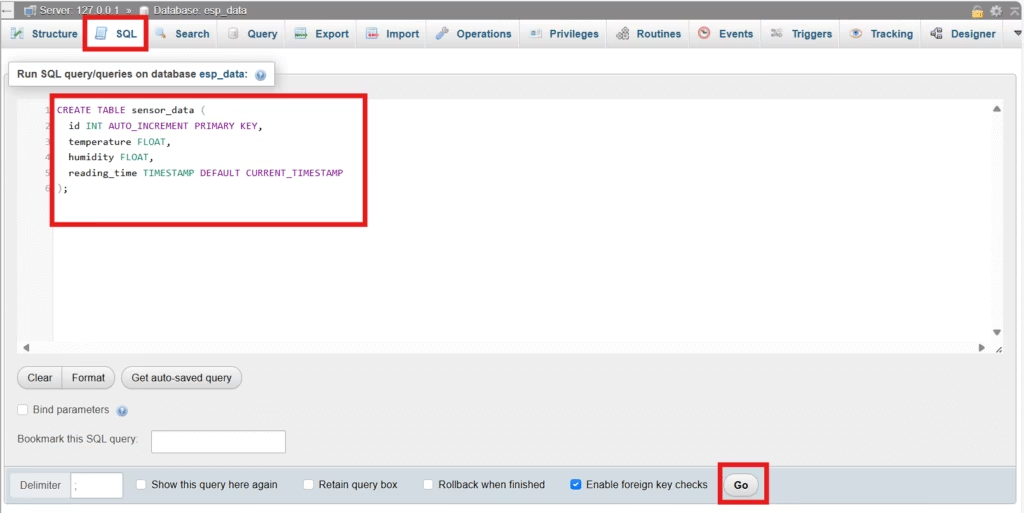
This table will store temperature and humidity values with a timestamp.
Step 2: Create PHP Script to Insert ESP32 Data in MySQL
Navigate to C:\xampp\htdocs\ and create a new file called insert.php. Add the following code:
<?php
$servername = "localhost";
$username = "root";
$password = "";
$database = "esp_data";
$conn = new mysqli($servername, $username, $password, $database);
if ($conn->connect_error) {
die("Connection failed: " . $conn->connect_error);
}
$temperature = $_GET['temperature'];
$humidity = $_GET['humidity'];
$sql = "INSERT INTO sensor_data (temperature, humidity) VALUES ('$temperature', '$humidity')";
if ($conn->query($sql) === TRUE) {
echo "Data inserted successfully";
} else {
echo "Error: " . $conn->error;
}
$conn->close();
?>
This script receives temperature and humidity from the ESP32 and inserts them into the database.
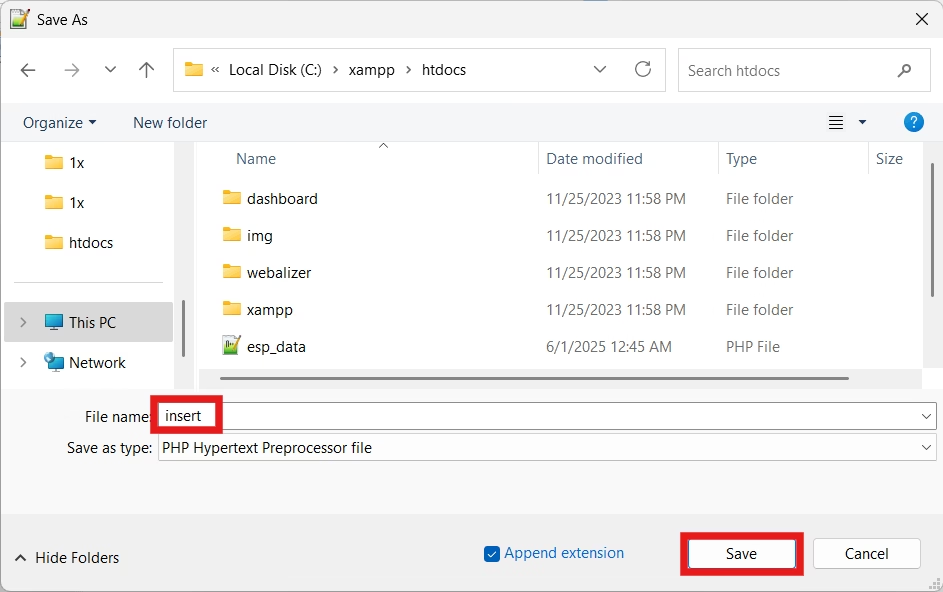
Step 3: Write ESP32 Code to Send Data
Open Arduino IDE and upload the following sketch to your ESP32.
//ESP32 Data in MySQL Database table
#include <WiFi.h>
#include <HTTPClient.h>
#include "DHT.h"
#define DHTPIN 27 // Connect DHT11 data pin to GPIO 27 (change if needed)
#define DHTTYPE DHT11 // Define sensor type DHT11
DHT dht(DHTPIN, DHTTYPE);
const char* ssid = "YOUR_WIFI_SSID";
const char* password = "YOUR_WIFI_PASSWORD";
String serverName = "http://192.168.1.100/insert.php"; // Replace with your PC's IP
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
dht.begin(); // Initialize DHT sensor
WiFi.begin(ssid, password);
while (WiFi.status() != WL_CONNECTED) {
delay(1000);
Serial.println("Connecting to WiFi...");
}
Serial.println("Connected to WiFi");
}
void loop() {
float temperature = dht.readTemperature(); // Celsius
float humidity = dht.readHumidity();
// Check if readings are valid
if (isnan(temperature) || isnan(humidity)) {
Serial.println("Failed to read from DHT sensor!");
delay(5000);
return;
}
// Print values to Serial Monitor
Serial.print("Temperature: ");
Serial.print(temperature);
Serial.println(" °C");
Serial.print("Humidity: ");
Serial.print(humidity);
Serial.println(" %");
if (WiFi.status() == WL_CONNECTED) {
HTTPClient http;
String postData = "temperature=" + String(temperature, 2) + "&humidity=" + String(humidity, 2);
http.begin(serverName+"?"+postData);
int responseCode = http.POST("");
if (responseCode > 0) {
String response = http.getString();
Serial.println("Server Response: " + response);
} else {
Serial.println("Error sending data to server.");
}
http.end();
} else {
Serial.println("WiFi not connected");
}
delay(10000); // Wait 10 seconds before sending again
}
Replace
192.168.1.100with your actual PC IP address (useipconfigin CMD to find it). Add your SSID and Password in code.
Setting Up the Arduino IDE
1. Installing ESP32 boards in arduino IDE
Before starting, make sure you have the ESP32 boards installed in your Arduino IDE:
How To Install ESP32 And ESP8266 Boards In Arduino IDE (Step-by-Step Guide) – ArduinoYard
2. Install Required Libraries
Make sure you have the following libraries installed in your Arduino IDE:
In Arduino IDE, Go to Sketch > Include Library > Manage Libraries.
- Search for DHT Sensor Library (for reading data from the DHT11).

WIRING DIAGRAM
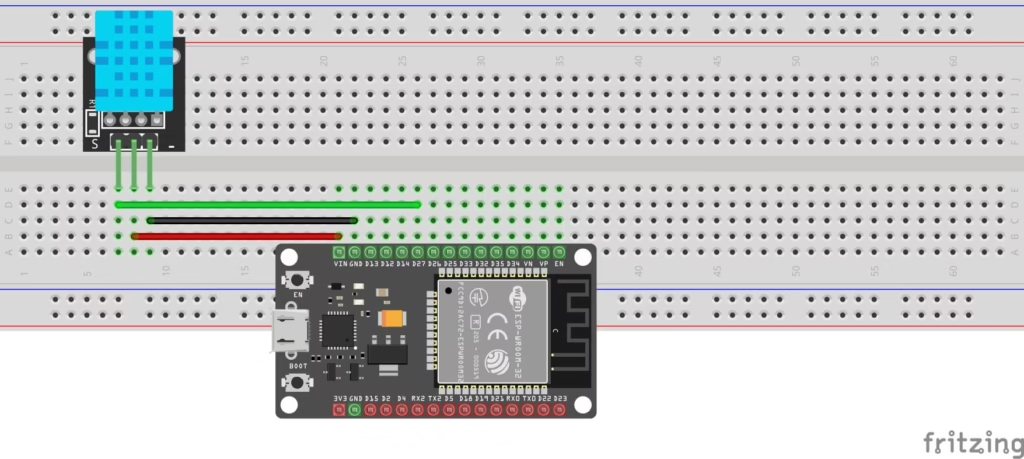
- Connect the VCC pin of the DHT11 to the VIN pin of the ESP32.
- Connect the GND pin of the DHT11 to the GND pin of the ESP32.
- Connect the Data pin of the DHT11 to GPIO 27 of the ESP32.
Step 4: Test and View ESP32 Data in MySQL
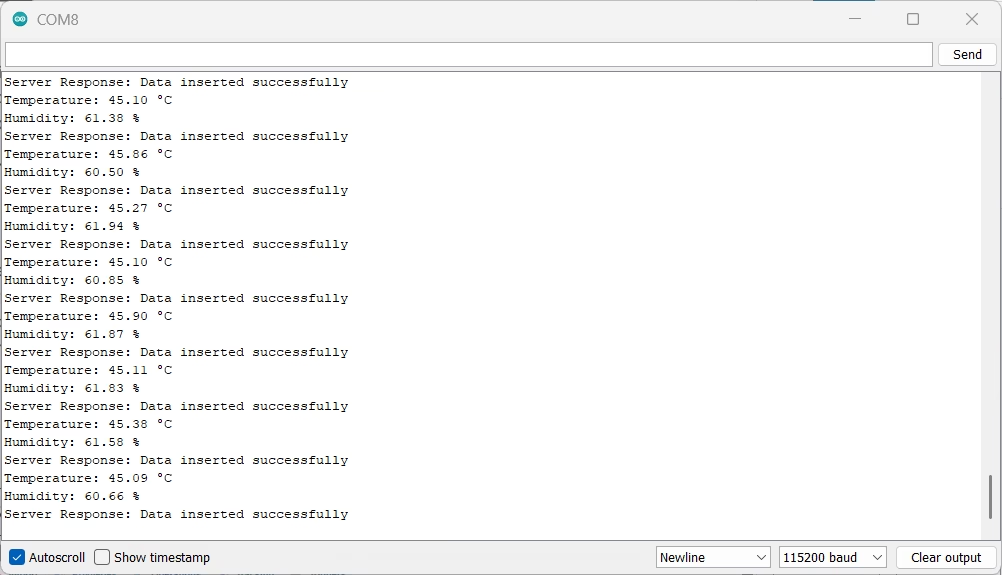
- Upload the code in your ESP32 and open the Serial Monitor
- Ensure it connects to Wi-Fi and sends a POST request every 10 seconds
- Visit
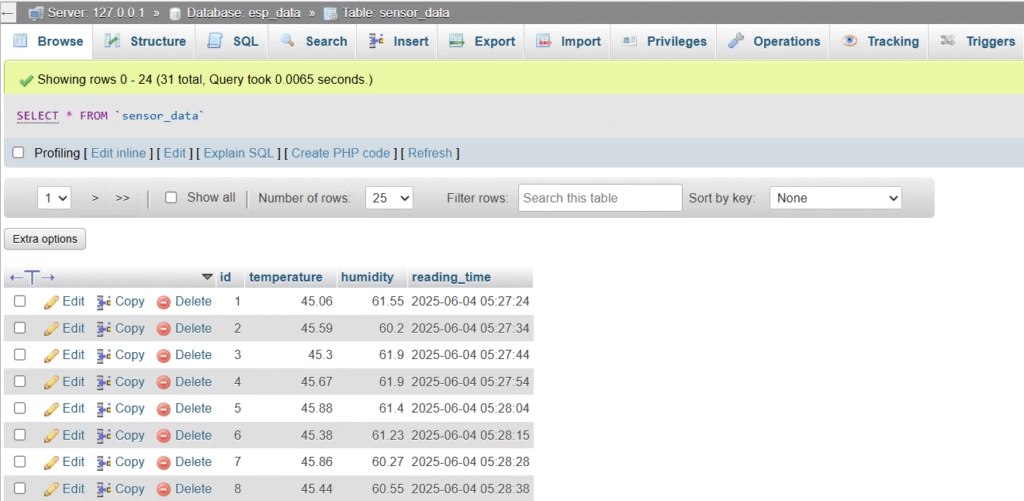
http://localhost/phpmyadmin, openesp_datadatabase - Check the
sensor_datatable to see values being inserted in real-time
Now your ESP32 data in MySQL is being stored successfully using XAMPP.
Serial Monitor:
ESP32 Data in MySQL Table:
Troubleshooting Tips
- Error connecting to server: Double-check the server IP and that Apache is running
- No data in database: Check for SQL or PHP errors in the script
- ESP32 can’t connect to Wi-Fi: Ensure your SSID/password are correct
- Firewall blocking requests: Allow Apache and MySQL through Windows Firewall
Bonus: Visualize ESP32 Data from MySQL
You can now build a PHP-based dashboard using Chart.js or Google Charts to graph the ESP32 data in MySQL in real time. This turns your local server into a live monitoring system for temperature, humidity, or any other sensor values.
Conclusion
Storing ESP32 data in MySQL using XAMPP gives you a reliable and offline-friendly solution to manage your IoT project’s data. With just a few lines of PHP and a simple ESP32 sketch, you can build an entire data logging platform locally. This not only helps in rapid prototyping but also lays the groundwork for deploying larger-scale systems in the future.
Whether you are a student, hobbyist, or professional, learning to save ESP32 data in MySQL with XAMPP is a must-have skill in your IoT toolkit.
incase you missed the previous parts:
How To Install XAMPP Server On Windows: A Step-by-Step Guide – ArduinoYard
How To Connect ESP32 With XAMPP Server On Windows: An Easy Guide – ArduinoYard